- Simplifying AI
- Posts
- 🤖 Run NVIDIA’s new coding AI locally
🤖 Run NVIDIA’s new coding AI locally
PLUS: Meta trains AI to teach itself; xAI scales to city-level power; China treats AI as national infrastructure

Good Morning! A clear pattern is emerging. China is treating AI like national infrastructure, Meta is teaching models to improve themselves, and xAI is scaling compute to power-city levels. Plus, hands-on tutorial on running NVIDIA’s Nemotron model locally.
In today’s AI newsletter:
China Plans to Make AI Infrastructure
Meta Teaches AI to Learn Coding via Self-Play
xAI Expands “Colossus” to 2 Gigawatts
How to run NVIDIA’s open-source coding model locally on your PC
4 new AI tools worth trying

AI RACE
China’s upcoming five-year plan (due March 2026) points to a strategic shift toward large-scale AI deployment across the economy, treating AI less like a breakthrough tech and more like basic infrastructure.
“AI+” policy frames AI agents and smart devices as tools embedded into everyday workflows
Six priority sectors targeted for broad adoption by 2027, including industry, healthcare, education, and government
Goal is AI ubiquity by 2030, with an “intelligent society” vision by 2035
New regulations aim to manage risks from human-like, emotionally engaging AI systems alongside rollout
In AI, diffusion often beats invention. China is betting that widespread, coordinated deployment of “good enough” models can unlock massive productivity gains faster than chasing the cutting edge. The next chapter of the AI race may be won not on benchmarks, but on factory floors, classrooms, and public services.
AI RESEARCH
Meta released Self-play SWE-RL (SSR), a new training method where a single AI model improves its coding skills by generating its own bugs and then learning to fix them, no human-written issues required.
One model plays two roles: bug injector (creates realistic failures) and bug solver (repairs them)
On SWE-bench Verified, SSR gained 10+ points over its base model and beat human-data baselines
Failed repair attempts become “higher-order bugs,” automatically creating a harder curriculum
Training is grounded in real repositories, without curated issues or labels
Today’s coding agents are capped by human-generated data like GitHub issues. Self-play breaks that ceiling. If models can generate unlimited, increasingly difficult training problems on their own, software agents may improve the same way AlphaGo did, by learning faster than humans can teach.
AI NEWS
Elon Musk announced that xAI has acquired a third building near its Memphis data center, pushing the total capacity of its Colossus complex to nearly 2 gigawatts, positioning it as one of the largest AI training sites on Earth.
Third facility sits next to Colossus 2 and near a dedicated natural gas power station
Total capacity (~2GW) is enough to power ~1.5 million U.S. homes annually
Colossus 2 is expected to house 555,000+ Nvidia GPUs, costing ~$18B in chips alone
xAI plans wastewater recycling to reuse ~13M gallons/day amid heavy cooling demands
AI leadership is now an infrastructure race. By vertically integrating power, compute, and capital at unprecedented scale, xAI is betting that sheer training capacity will decide the next phase of model dominance, even as energy, water, and public scrutiny become the real bottlenecks.

HOW TO AI
🗂️ How to Run NVIDIA’s Nemotron Model Locally
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to run NVIDIA’s newly released Nemotron coding model entirely on your own machine using open-source tooling. By the end, you’ll have a production-grade AI model running locally on a standard gaming PC, capable of advanced reasoning, debugging real code, and even exposing an API for tool use.
🧰 Who is This For
Developers who want a powerful coding model without monthly subscriptions
Researchers experimenting with open-source LLMs and inference engines
Engineers who want full control over models, data, and deployment
Anyone curious about running state-of-the-art AI fully offline
STEP 1: Prepare Your System and Install the Inference Engine
To run Nemotron locally, you’ll use llama.cpp, a high-performance C/C++ inference engine designed to run large models efficiently on CPUs and GPUs. Start by opening your terminal and updating your system so it’s ready to compile native software.
Run the following commands to install the required build tools and utilities. These ensure your environment can compile and run llama.cpp without issues.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install build-essential git curl wget -yNext, download the llama.cpp source code directly from GitHub and move into the project directory.
git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
cd llama.cppNow compile the engine. This step builds the core binaries that will run the model. The build process may take a few minutes depending on your CPU.
make -jOnce this finishes without errors, your local AI runtime is fully set up.
STEP 2: Download and Run the Nemotron Model Locally
With llama.cpp installed, you can now download and launch the Nemotron model directly from Hugging Face using the built-in CLI tool. You don’t need to manually handle large model files, the engine does this for you.
Run the following command from inside the llama.cpp directory.
./llama-cli -hf unsloth/nvidia-Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct-HF-GGUF \
-m Nemotron-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-HF-Q4_K_M.gguf \
-p "You are a helpful assistant." \
-cnvThis command tells llama.cpp where to fetch the model from, which quantized version to use, how the assistant should behave, and to launch in conversational mode. The first run will take time as the model downloads. Once complete, you’ll see an interactive prompt ready for input.
If you have a compatible GPU, layers will automatically offload to it. If not, the model will still run fully on CPU, just more slowly.
STEP 3: Test Reasoning and Coding Capabilities
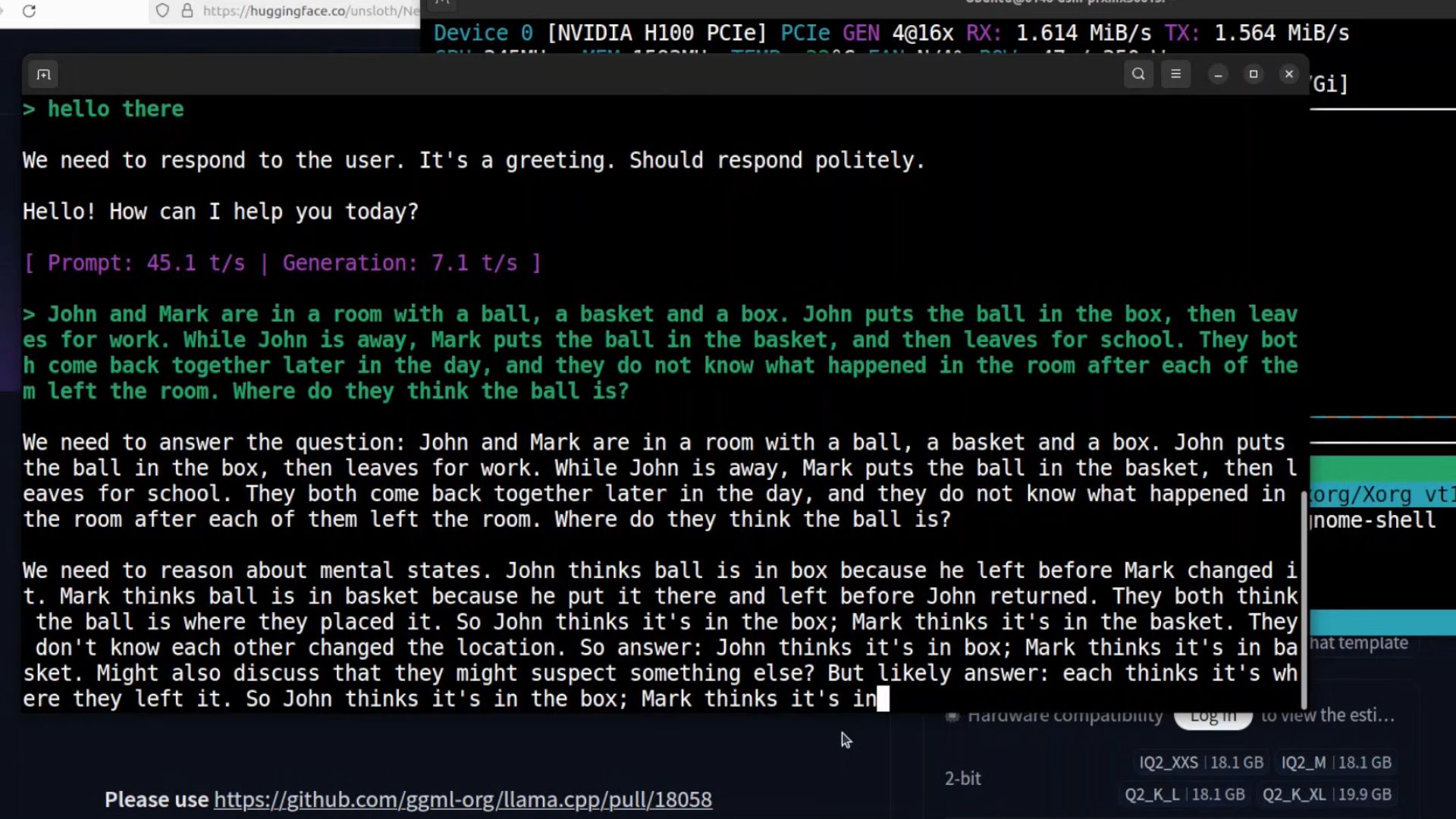
Once the model is running, you can begin testing its reasoning and coding skills directly in the terminal. Nemotron is particularly strong at logical inference and structured problem solving.
Try pasting a reasoning prompt that requires understanding different mental states, such as a logic puzzle involving multiple people and actions. You’ll notice the model carefully breaks down each perspective before arriving at an answer.
You can also test real coding tasks. Paste broken or legacy code, such as COBOL or enterprise scripts, and ask the model to debug it. The model will analyze the syntax, identify logic errors, and often explain the fix step by step, making it useful even for obscure or older programming languages.
This is where Nemotron starts to feel competitive with top paid coding assistants, despite running entirely offline.
STEP 4: Enable Advanced Tool Use with Server Mode
For more advanced workflows, you can run Nemotron in server mode. This turns your local machine into an API endpoint, similar to a hosted AI service, allowing external programs to send requests and define tools or functions the model can call.
Open a new terminal window, navigate back to the llama.cpp directory, and start the server with the following command.
./llama-server -hf unsloth/nvidia-Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct-HF-GGUF \
-m Nemotron-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-HF-Q4_K_M.gguf \
--port 8001 \
--ctx-size 8192This launches a local web server on port 8001. Your Nemotron model is now accessible at a local API endpoint, which means you can connect it to Python scripts, automation tools, or agent frameworks using OpenAI-compatible libraries.
At this point, you’re no longer just running a model, you’re operating your own fully local AI system, built on open infrastructure, with zero vendor lock-in.

China's draft AI rules have measures to protect kids, like time limits and parental consent, ban gambling promotion content, and add suicide chats restrictions.
Nvidia is in advanced talks to acquire Tel Aviv-based AI21, which is building its own LLMs, for $2B to $3B; the deal would resemble an acquihire.
SoftBank says it has completed a $22.5B investment in OpenAI, finalizing its up to $40B investment commitment announced in March and taking its stake to ~11%.
China is requiring chipmakers to use at least 50% domestically made equipment for adding new capacity, in a rule that is not publicly documented.

🧑💻 MiniMax 2.1: Strong model for coding and building apps
⚙️ GLM-4.7V: Zhipu AI’s open-source multimodal model
🤖 Nemotron 3: Nvidia’s open-source models for building multi-agent systems
⚙️ Antigravity: Google’s platform for building AI agents


THAT’S IT FOR TODAY
Thanks for making it to the end! I put my heart into every email I send, I hope you are enjoying it. Let me know your thoughts so I can make the next one even better!
See you tomorrow :)
- Dr. Alvaro Cintas